Create a trigger
A trigger is an event that may occur during a visit. Triggers help you target visitors depending on where, when, and how they interact with you website.
You can create, modify, and duplicate triggers using Kameleoon's Trigger Builder.
Access the Trigger Builder
From the app
To access the Trigger Builder from the Kameleoon app:
- Click Settings > Triggers > New Trigger.
The Trigger creation pop-in opens.
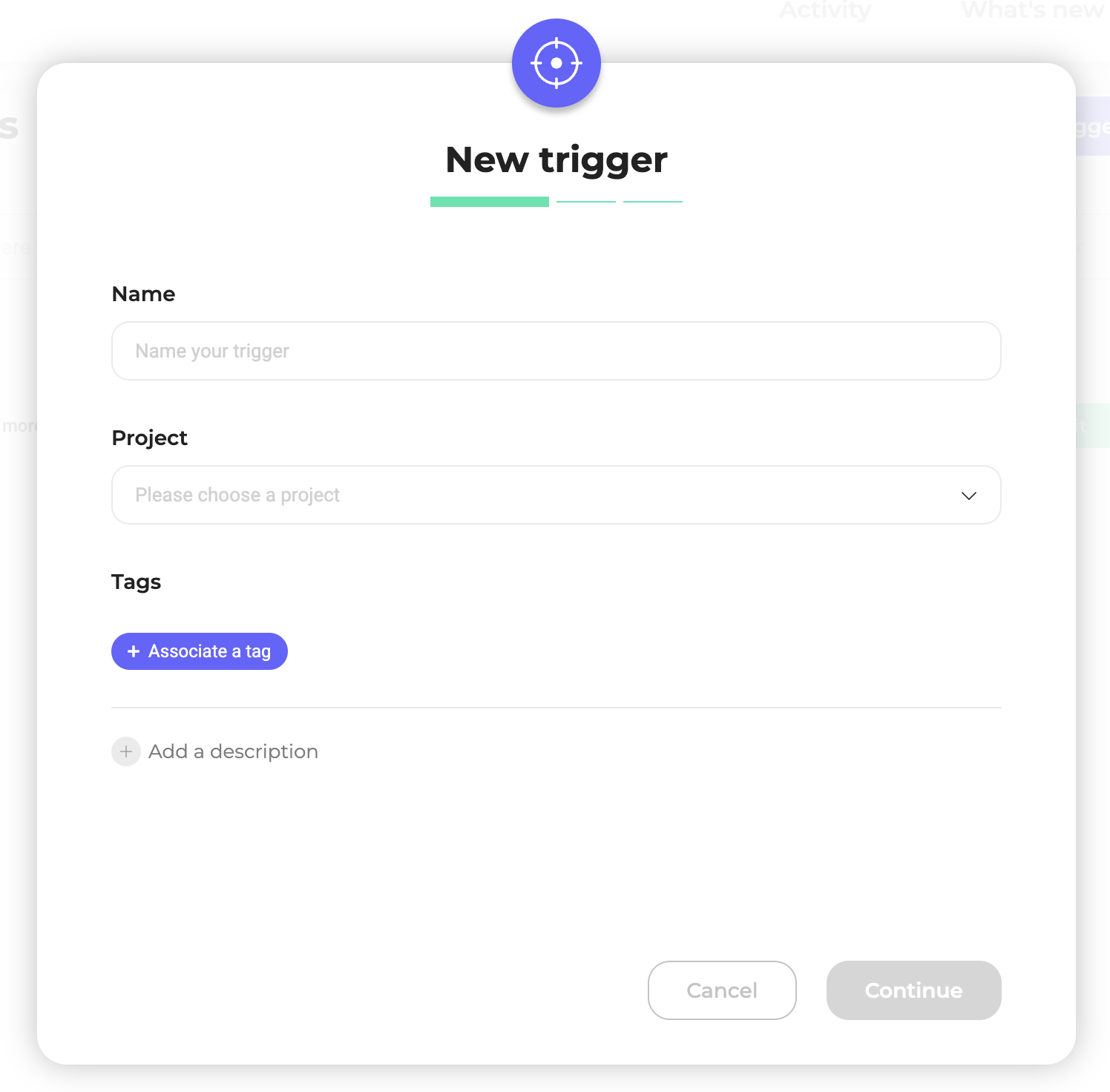
Create a new Trigger
Later this year, segments and triggers will have separate sets of conditions. Some conditions found in the segment builder (for example, those that describe how, where, and when a visitor interacts with a website) will be moved to the Trigger Builder. Existing segments will remain unchanged and continue to function in experiments. However, new segments and triggers will follow this new separation. Help will be provided to facilitate transition from the old system to the new one.
Enter your Trigger's information
You must provide the following information:
- Your trigger's name
- The site for which you are creating this trigger
- The trigger's description and tags (optional)
Set a condition
To add a condition, drag and drop a condition from the left-hand list to the field on the right.
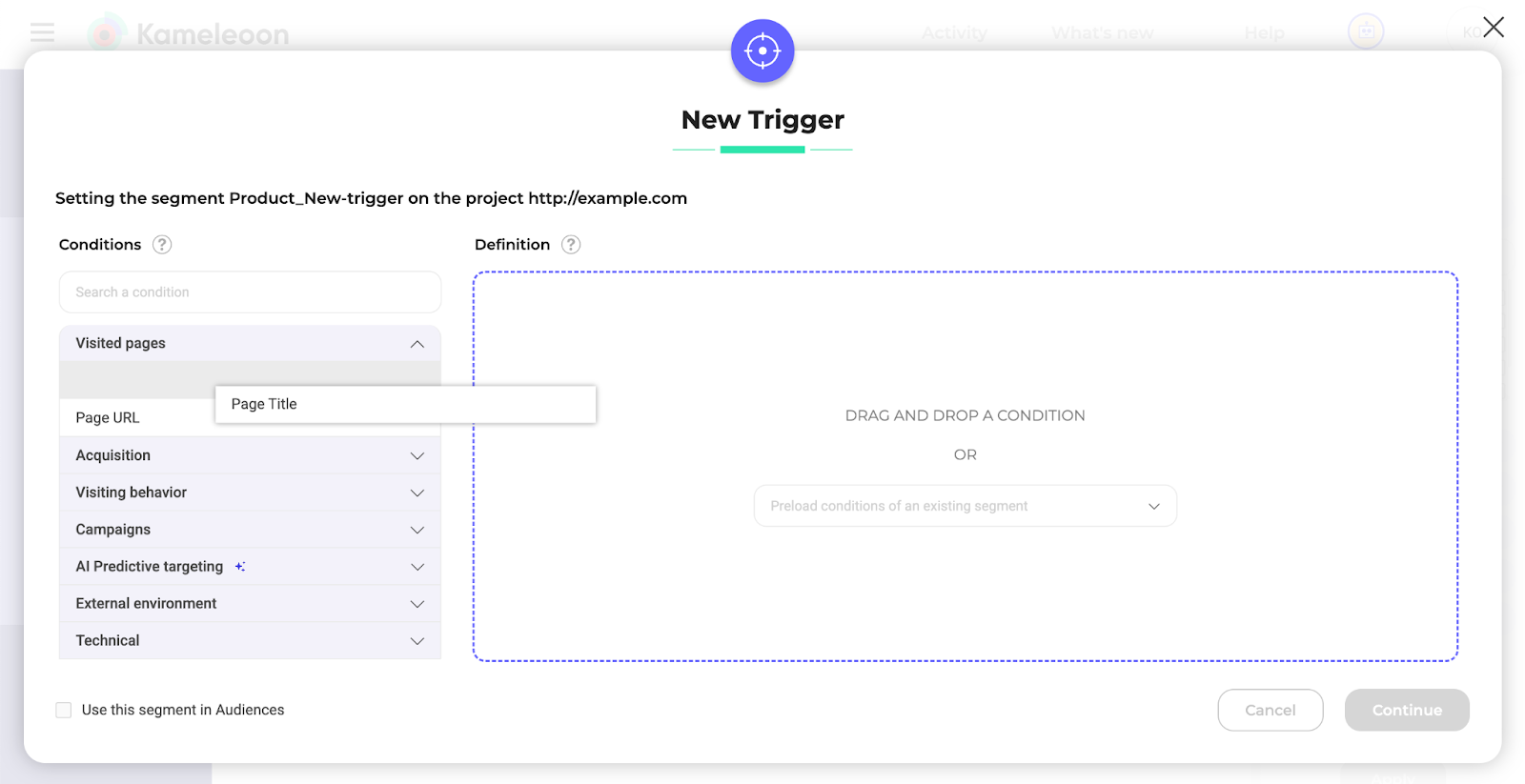
Determine its weight
Use the weight icon to prioritize a condition: a higher number means higher priority. This setting is not mandatory.
All conditions have a default weight of one.
You can learn more about weight in the FAQ
Delete a condition
Click the X icon to delete a condition.
Narrow or add a condition
To add a new condition when you've already selected a condition, two options are available:
- Narrow an existing condition: Further specifies a condition, similar to using mathematical parentheses: (Condition A and Condition B) and Condition C.
- Add a new condition: Adds a condition at the same level: Condition A and Condition B and Condition C.
Use logical links between conditions
Creating effective targeting triggers in Kameleoon involves combining various conditions to define your audience. The use of the logical operators AND/OR is crucial in this process. Additionally, understanding the distinction between “include” and “exclude” conditions is essential for accurate trigger configuration.
Logical operators: AND vs. OR
AND Operator: Use the AND operator when you want all specified conditions to be met for a visitor to be included in your trigger. This operator is ideal for narrowing your target audience to those who meet all of your defined criteria.
- Example: If you set an AND condition for visitors who are on a specific "Page URL" AND coming from a “Referring website URL”, only visitors who are both arriving at the page URL and coming from the referring website URL will be included in the trigger.
OR Operator: Use the OR operator when you want a visitor to meet any one of the specified conditions to be included in your trigger. This operator broadens your target audience to include visitors who meet any one of your criteria.
- Example: If you set an OR condition for visitors who are on a specific "Page URL" OR coming from a “Referring website URL”, visitors who are either arriving at the page URL or coming from the referring website URL will be included in the trigger.
AND is prioritized over OR.
Include vs. exclude conditions
Include Condition: Specifying an “include” condition means that you want visitors who meet this condition to be part of your trigger.
- True: Visitor possesses the characteristic (for example, “lands on a page that corresponds exactly to the URL” is true).
- False: Visitor does not possess the characteristic (for example, “lands on a page that corresponds exactly to the URL” is false).
Exclude Condition: Specifying an “exclude” condition means that visitors who meet this condition will not be part of your trigger.
- True: Visitor does not possess the characteristic (for example, “lands on a page that corresponds exactly to the URL” is true, meaning they are on the page, so they are excluded).
- False: Visitor possesses the characteristic (for example, “lands on a page that corresponds exactly to the URL” is false, meaning they are not on the page, so they are included).
Practical examples and common pitfalls
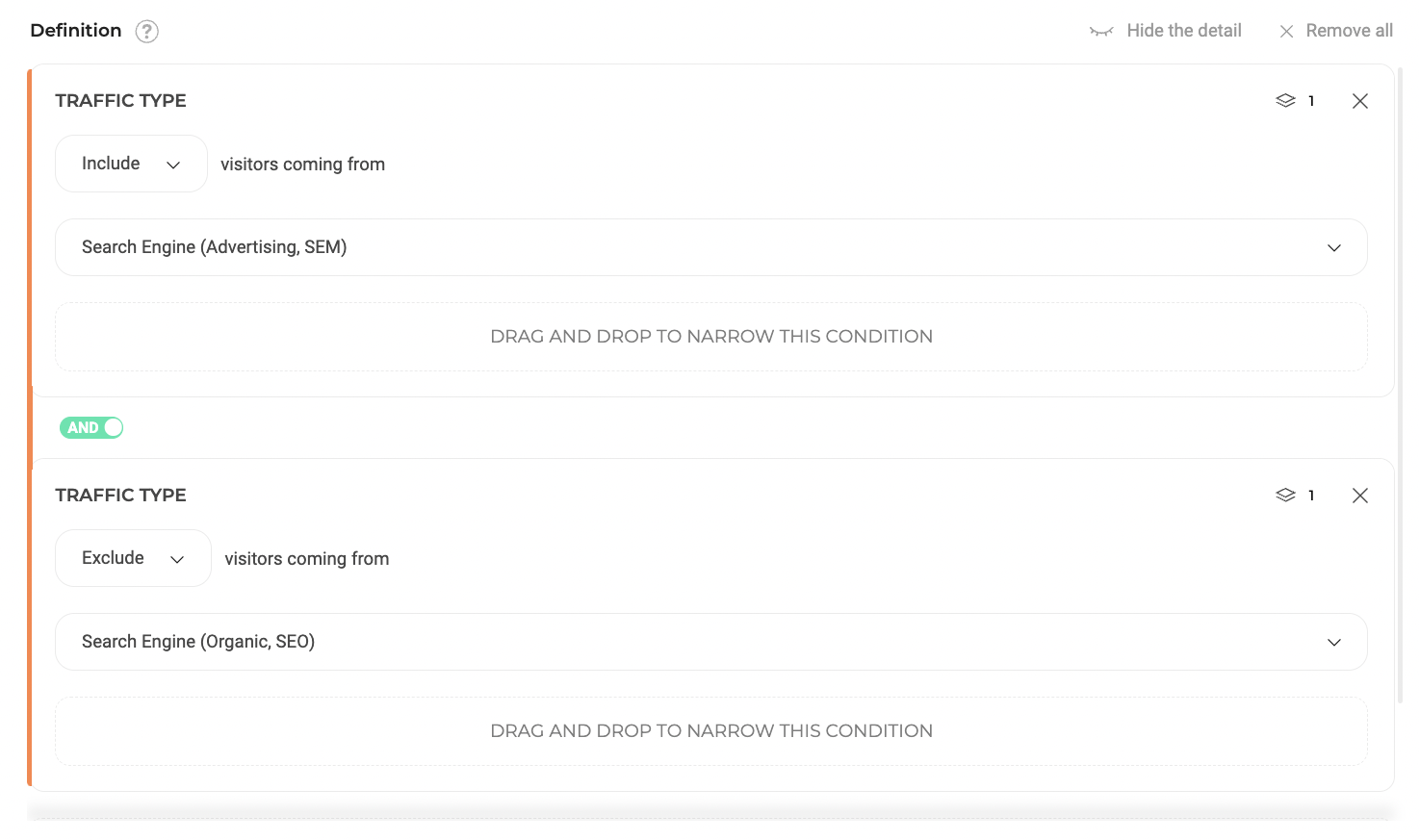
- Including Visitors from Specific Acquisition Channels:
- Condition 1: Acquisition Channel is SEO (Exclude, True)
- Condition 2: Acquisition Channel is SEA (Include, True)
- Logical Link: AND
- Outcome: Only visitors arriving from SEA campaigns and not SEO will be included in the experiment.
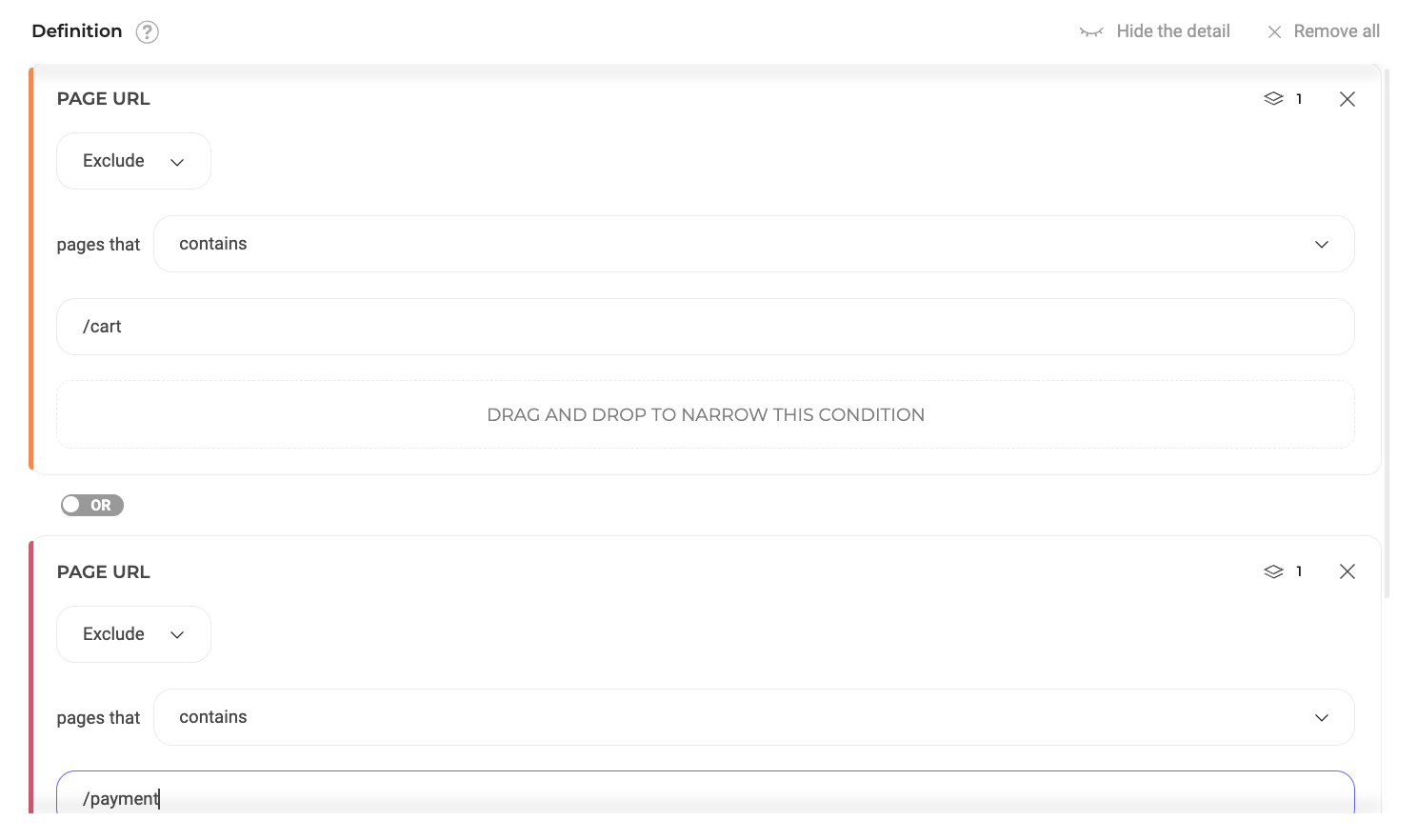
- Excluding Checkout Process Pages:
- Condition 1: URL contains /cart (Exclude, True)
- Condition 2: URL contains /login (Exclude, True)
- Condition 3: URL contains /payment (Exclude, True)
- Logical Link: OR
- Outcome: Pages related to the checkout process will be excluded from the experiment.
Consider the impact of logical operators in conjunction with include/exclude conditions when configuring your targeting triggers. Remember that include conditions add visitors to your trigger based on positive criteria matches, while exclude conditions remove visitors who meet specific criteria. The choice between AND/OR operators can significantly alter your trigger's scope, either narrowing or broadening the range of included visitors.
If you’re not sure if you’ve set everything up correctly, use our simulation panel.
Targeting conditions
Kameleoon offers a variety of targeting conditions to help you include or exclude visitors.
The targeting conditions available in the Trigger Builder depend on the chosen campaign type.
Visited pages
- Page URL: Includes or excludes pages based on their URL or URL fragment.
- Page Title: Includes or excludes pages by title.
You can target one or several pages using these two options, which can be useful if you want to change HTML elements shared by several pages. If you want to target a page's URL or title, Kameleoon only displays the variation for users of these pages.
You can target any URL using regular expressions. For more information on regular expressions, read this article.
If you're using the Contains targeting option and your expression doesn't start with http or https, Kameleoon will only check the expression's presence after the domain name.
URL fragments are case-sensitive.
Acquisition
You can make commercial offers to users who searched for a specific keyword in their search engine or engaged with your marketing emails.
Take care when using the Visitor data and Traffic acquisition targeting options. These options are most useful for personalization (for example, displaying a commercial offer to non-buying regular visitors), and must be combined with another condition, such as URL targeting.
- Landing page URL: Includes or excludes visitors based on the URL of the page they land on.
- Referring URL: Includes or excludes visitors based on the referring URL.
- Acquisition channel: Includes or excludes visitors based on their acquisition channel.
- Traffic type: Includes or excludes visitors from specific sources (for example, search engine, emailing, website tributary).
The Traffic Type condition depends on either the Landing page URL or the Referrer URL:
- Emailing if the Landing page URL contains the pattern
utm_medium=emailorutm_medium=newsletter. - Search Engine (Advertising, SEM) if the Landing page URL is from a
googledomain and hasaclkas path, OR has the parameteraclkin the query. - Search Engine (Organic, SEO) if the Referrer URL contains
google,bing,yahoo,yandex, orbaidu. - Direct if the Referrer URL is empty (
null). - Referrer sites (Affiliation) if you have a Landing page URL and a Referrer URL that do not contain
google,bing,yahoo,yandex, orbaidu.
Visiting behavior
- Website exit: Includes or excludes visitors whose cursor has left the browser window.
- Goal converted: Includes or excludes visits during which a specific goal was converted.
- Pages viewed
- Previous page: Includes or excludes visitors based on the previous page's URL.
- Number of page views: Includes or excludes visitors based on the number of pages previously visited.
- Product pages
- Price of the product page displayed: Includes or excludes product pages where price is higher than / lower than / equals a certain amount (a fixed price / the price of a specific product / the average price of a selection of products).
- Number of visited product pages: Includes or excludes visitors based on the number of product pages they visited, the category to which these pages belong, and their price.
- Visited product pages: Includes or excludes visitors based on the product pages they visited.
If you are using Shopify Plus, the Product Pages conditions are available without any additional configuration. Read our documentation
- Elapsed time
- Time elapsed since first visit: Includes or excludes visitors based on the time elapsed since their first visit.
- Time elapsed since last visit: Includes or excludes visitors based on the time elapsed since their last visit.
- Time elapsed since session became active: Includes or excludes visitors based on the time elapsed since the beginning of the session.
- Time elapsed since page load: Includes or excludes visitors based on the page loaded.
- Number of visits
- Number of visits today: Includes or excludes visitors based on their number of visits today.
- Total number of visits: Includes or excludes visitors based on the total number of their visits.
- Number of visits by page: Includes or excludes visitors based on their number of visits to a specific page.
Campaign
This set of conditions lets you include or exclude visitors who have or haven't seen a campaign (experiment/personalization) or variation.
- Experiment: Includes or excludes visitors who have been exposed to a specific experiment and have seen a specific variation OR any of the variations (original included). The condition considers the current or previous visits. The selected experiment can be Online, Paused, or Stopped.
- Feature Flag: Includes or excludes visitors who have been exposed to a specific Feature flag and have seen any of the variations, OR the On OR the Off flag, and have been assigned to any of the variations OR a specific variation.
- Personalization: Includes or excludes visitors who have been exposed to a specific personalization. The condition considers the current or previous visits. The selected personalization can be Online, Paused, or Stopped.
- Exclusive campaign: Excludes visitors already partaking in an experiment, a personalization, or both, meaning that:
- If a visitor has already been exposed to another campaign (in a current or previous visit), this visitor won’t be targeted in the current experiment.
- A visitor can be targeted by other experiments that do not have the Exclusive campaign condition, even if they are currently part of an exclusive campaign. In other words, this condition doesn’t prevent participation in other experiments. It lets visitors participate in experiments that don’t have the same exclusivity requirement.
Campaigns or variations can't be deleted if you're using them as a targeting condition in a segment.
- Exclusive Feature Flag: Excludes visitors already included in an ongoing Rollout or Feature/Web experiment, meaning:
- If a visitor is already exposed to another Flag (in the current or previous visit), this visitor won’t be eligible.
- A visitor can be targeted by other experiments/rollout/flags that do not have the Exclusive Feature Flag condition, even if they are currently part of an exclusive Feature flag. In other words, this condition does not prevent participation in other Flag experiments. It lets visitors participate in experiments that don’t have the same exclusivity requirement.
AI Predictive targeting
- Kameleoon Conversion Score: Our machine-learning algorithms predict each visitor’s purchase or engagement intention in real-time. You can use Likelihood to convert to automatically trigger personalization campaigns.
You need AI Predictive Targeting to activate likelihood to convert.
External environment
- Weekday: Includes or excludes visitors on a specific day of the week
- Date range: Includes or excludes visitors to the website during a given date range.
- Time slot: Includes or excludes visitors within a given time period.
- Weather
- Current weather
- Sky condition: Includes or excludes visitors according to the weather in their location.
- Temperature: Includes or excludes visitors based on their location's temperature.
- Day / Night: Includes or excludes visits during the day or night.
- Weather forecast
- Sky condition forecast: Includes or excludes visitors whose location has the following sky conditions.
- Temperature forecast: Includes or excludes visitors whose location has the following temperatures.
- Current weather
Technical
- Custom JavaScript condition: You can write a custom JavaScript function that will return True or False. If the result is True, the visitor is included in the experiment. This function can be evaluated each time the page is displayed, or asynchronously.
- Check condition immediately or when the page has loaded: If
undefinedis returned, the code will retry execution every 75 ms for the first 3 seconds, then every 250 ms. - Run the condition asynchronously: Your JavaScript is evaluated for each experiment.
- If you want to return
trueorfalsedepending on a variable's value in your data layer, you can use this code (which you need to adapt depending on your data layer name):
- Check condition immediately or when the page has loaded: If
if (typeof utag_data != "undefined" && typeof utag_data.is_logged_in != "undefined" && utag_data.is_logged_in != ""){
if (utag_data.is_logged_in == "false")
return false;
else
return true;
}
return undefined; // will loop until utag_data and utag_data.is_logged_in is defined
If you are using the asynchronous condition, the callback function is setTargeting. You need to replace it in the code: setTargeting(true) / setTargeting(false)
- Browser cookie: Includes or excludes visitors based on a cookie's presence in their browser and, if possible, its value.
- Custom event: Starts a personalization only when a specific event has been triggered. To trigger an event, use the
Kameleoon.API.Events.trigger(eventName)method. - Explicit trigger: Explicitly triggers a campaign using our Activation API. Use explicit triggers for campaigns you implement with a modern JS framework (for example, React, Vue, Angular).
- Element on the page: Includes or excludes visits based on an element's presence on the page. The condition performs a
querySelectorAllloop until the DOM ready event. After that, the condition returnsfalse.
Associate goals with your trigger (optional)
You can associate goals with your trigger in the Trigger Builder's last step. You can see the goals on which you enabled machine learning in the list displayed.
Once you link a goal to your trigger, the algorithm's training activates, allowing it to target users based on their likelihood to convert on a goal.